Experiencing heartburn on occasion is perfectly normal, especially if you eat triggering foods. Unfortunately, sometimes a more serious condition known as gastroesophageal reflux disease can be the actual culprit. If left untreated, you can experience symptoms more frequently as well as other complications that may require surgical treatment.
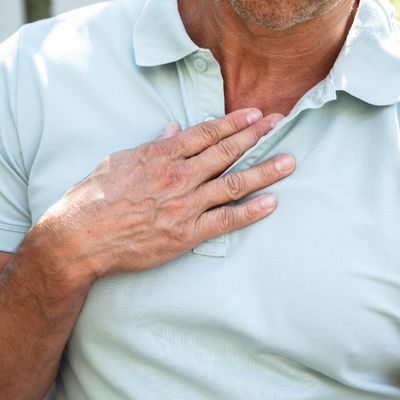

Gastroesophageal reflux disease is the inflammation of the lining of the esophagus due to exposure to stomach acids. Common symptoms include heartburn, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing. It’s caused by a malfunctioning valve in the lower esophagus and can lead to more severe issues later on if not properly treated. It can be diagnosed and treated in a number of ways including surgery if other methods aren’t successful.
What is GERD?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is the result of stomach acids moving up into the esophagus that connects your stomach and mouth. Over time, the lining of your esophagus can become irritated by repeated exposure to the backwash of stomach acid (acid reflux).
Click here to learn 4 ways that hepatobiliary surgery can help with gastrointestinal issues!
Symptoms of GERD
Symptoms of GERD can vary from patient to patient. Common symptoms of GERD include:
- Heartburn
- Feeling like food is caught in your throat
- Chest pain
- Vomiting
- Coughing
- Trouble swallowing
- Hoarseness and sore throat
- Regurgitation
GERD symptoms can vary from night to day. For instance, common symptoms of nighttime acid reflux include:
- Inflamed vocal cords (laryngitis)
- New or more severe asthma
- Continuous cough
To learn when surgery may be necessary for your child, click here!
Causes
GERD is caused by a malfunctioning valve at the lower end of your esophagus (esophageal sphincter). When working, it will naturally close properly on its own when food enters your stomach. However, a malfunctioning valve will remain open and allow food along with other stomach contents to move back up the esophagus and into your throat and mouth.
It’s perfectly normal to experience acid reflux at some point in life and it is usually no cause for alarm. It, along with heartburn, are completely normal experiences. On the other hand, you may have a more serious problem if you are experiencing:
- Acid reflux and heartburn two or more times per week over the span of several weeks
- Recurring acid reflux and heartburn despite regularly taking antacids and medications
These problems may indicate that you have developed GERD. You will need to speak with your healthcare provider at this stage. They will be able to provide a treatment plan that relieves your symptoms as well as prevents further complications.
Complications

Also known as chronic acid reflux, GERD can lead to complications if not treated in a timely manner. This includes problems such as:
- Esophagitis
- Esophageal stricture
- Barrett esophagus
Esophagitis occurs when the tissue in the esophagus becomes inflamed. The acids from the stomach break down the esophageal tissue leading to inflammation, bleeding, and possibly ulcers. It can also result in pain and make it more difficult to swallow.
Esophageal stricture is the narrowing of the esophagus. It’s caused by the lower part of the esophagus being damaged by stomach acids and the formation of scar tissue. This causes the food pathway to become narrow and can lead to difficulty swallowing.
Barrett esophagus involves precancerous changes to the esophagus. The lining of the lower esophagus is changed by stomach acids over time which can increase your risk of esophageal cancer.
Diagnosing & Treating GERD
If you suspect you may have GERD then you will need to see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis. If so, they will provide a treatment plan to help alleviate your symptoms and prevent any further complications.
Diagnosis
GERD can be diagnosed a number of ways. This includes:
- Upper endoscopy
- Ambulatory acid (pH) probe test
- X-rays of the upper gastrointestinal (GI) system
- Esophageal manometry
For upper endoscopy, your doctor will insert a thin tube down your throat with a camera and light on the end. This allows them to examine the inside of your esophagus and stomach for signs of GERD. The ambulatory acid (pH) probe test involves placing a monitor on your esophagus to determine how long stomach acids remain there.
X-rays of the upper GI system can detect GERD symptoms when combined with drinking a special liquid and taking a barium pill. Esophageal manometry measures muscle contractions when you swallow as well as the coordination and force exerted by the muscles in the esophagus.
Treatment
Doctors are likely to recommend lifestyle changes before medication and surgery. They may encourage you to:
- Lose weight
- Avoid eating before bed
- Wear loose clothing
- Sleep with your head elevated
- Eat small meals more frequently rather than large meals
- Cut out triggering foods
Your doctor may recommend over-the-counter (OTC) medications if your symptoms don’t clear up after making lifestyle changes. This can include antacids and acid blockers. Many of these medications are also available in stronger doses with a prescription from your doctor.
Surgery will be recommended if a combination of lifestyle changes and medications fail to relieve your GERD symptoms. Surgical options include laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Also known as Nissen fundoplication, it is the standard surgical treatment for GERD. This minimally invasive treatment works by creating a new valve mechanism at the bottom of your esophagus.
Do you need surgical gastroesophageal reflux disease Treatment in Evansville, IN? Contact us today to schedule your appointment!
Evansville Surgical Associates has been providing comprehensive and compassionate surgical care for over 50 years. Call us at (812) 424-8231 or (800) 264-8231. We are available from 8:00 am to 4:30 pm if you would like to schedule an appointment.